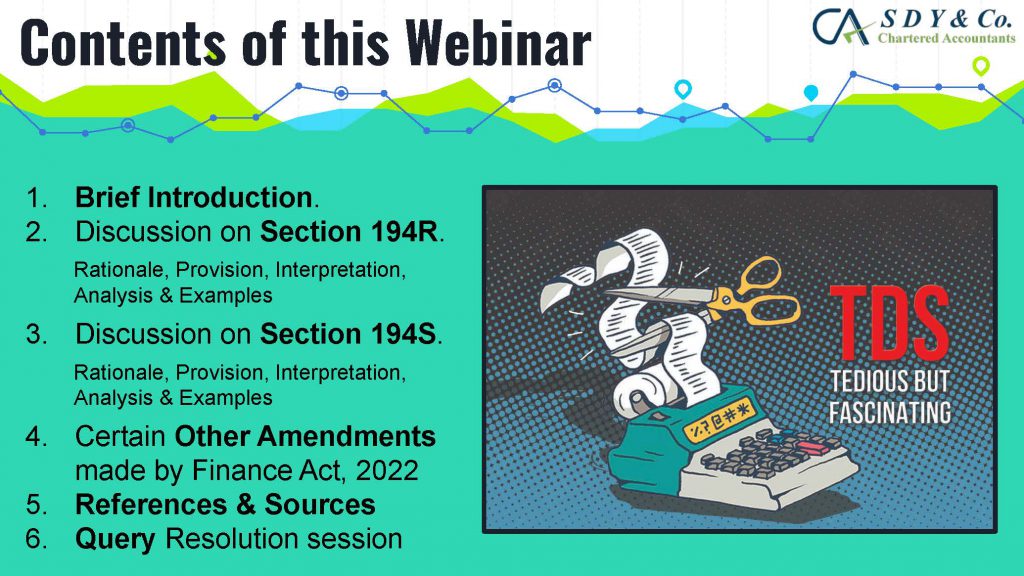
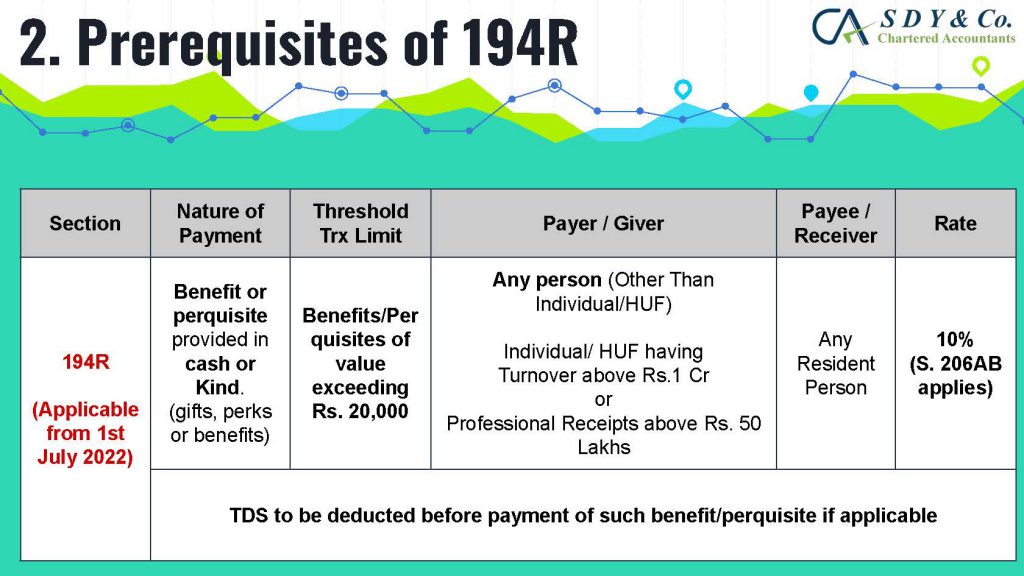
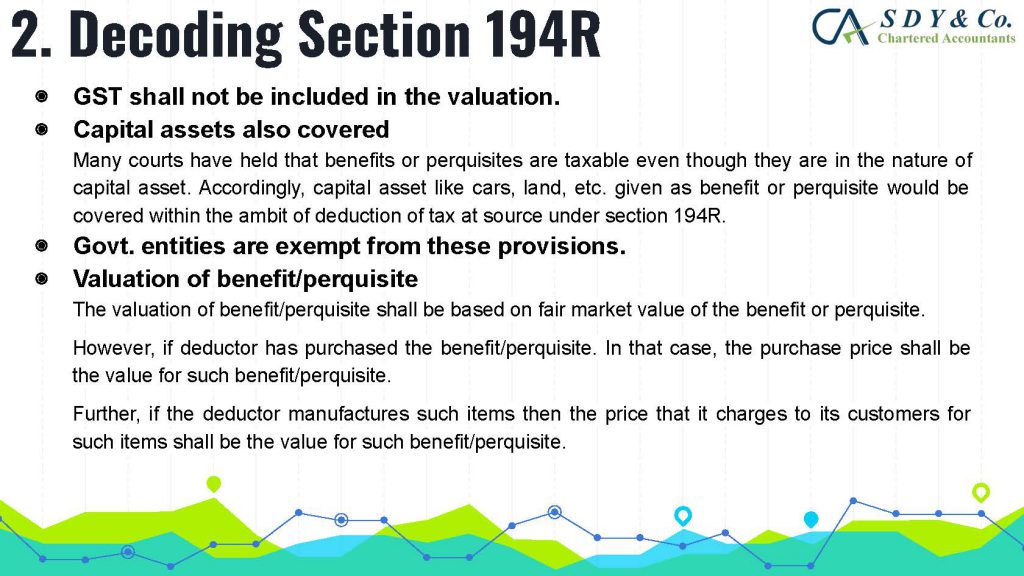
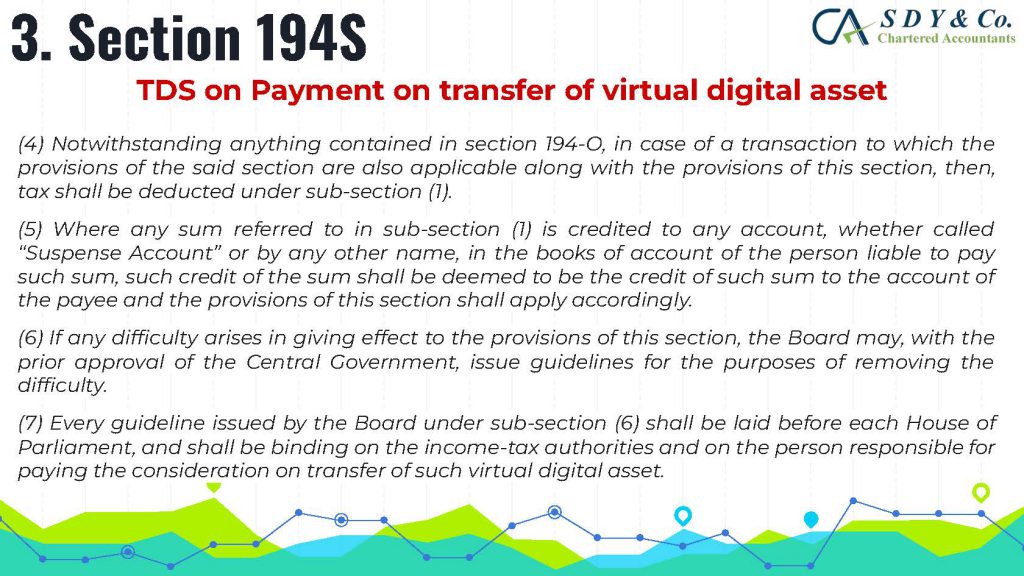
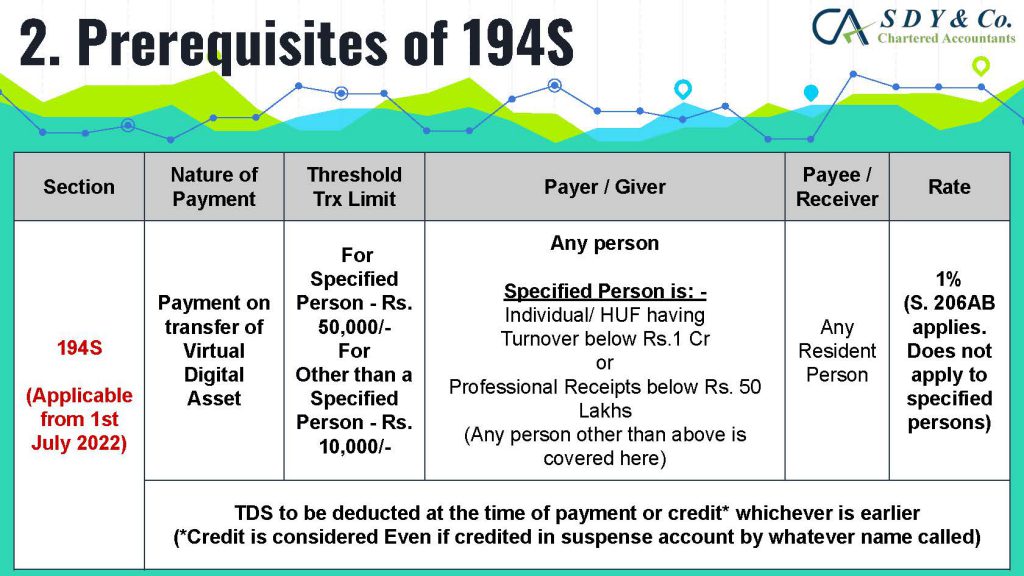
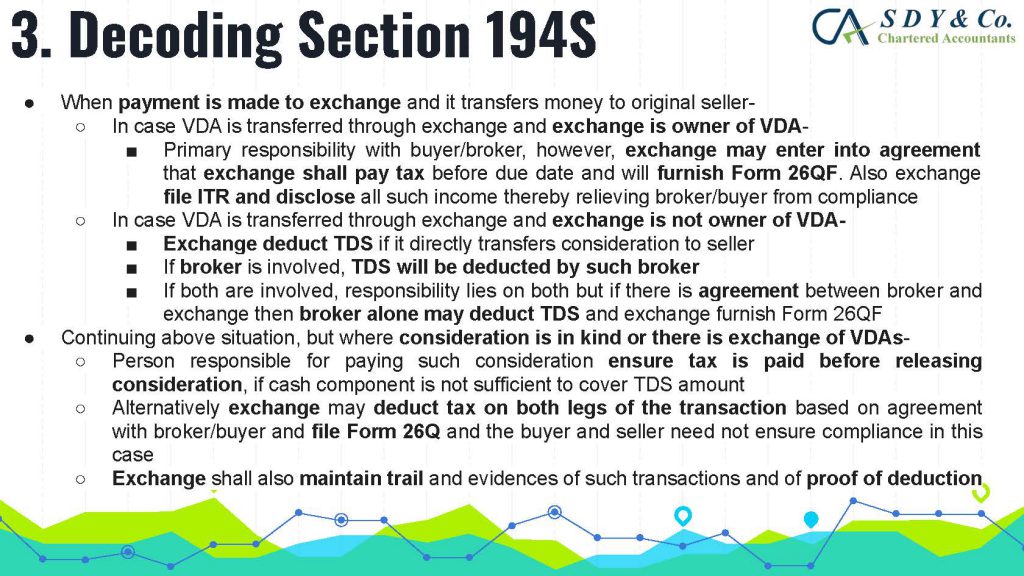
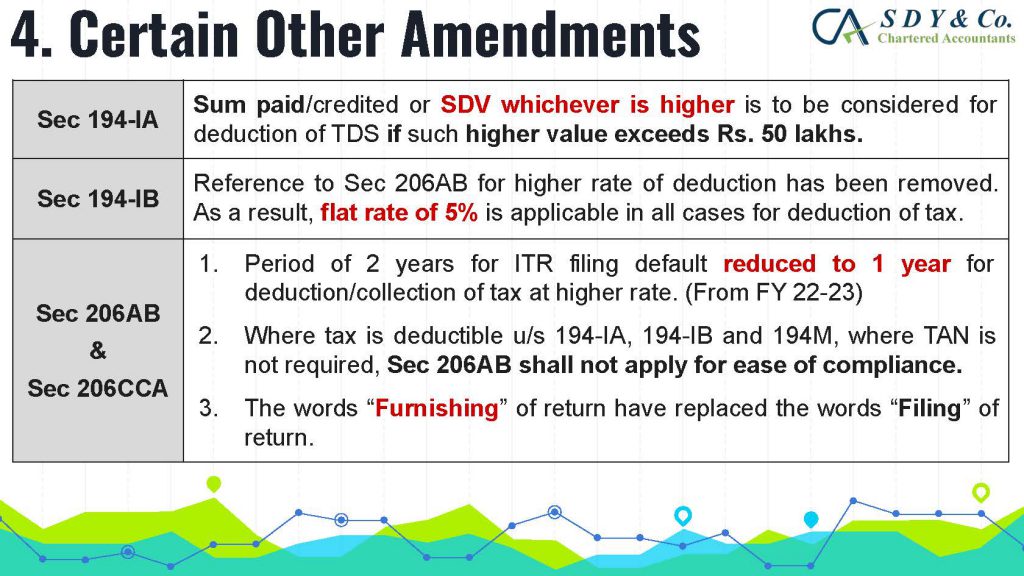
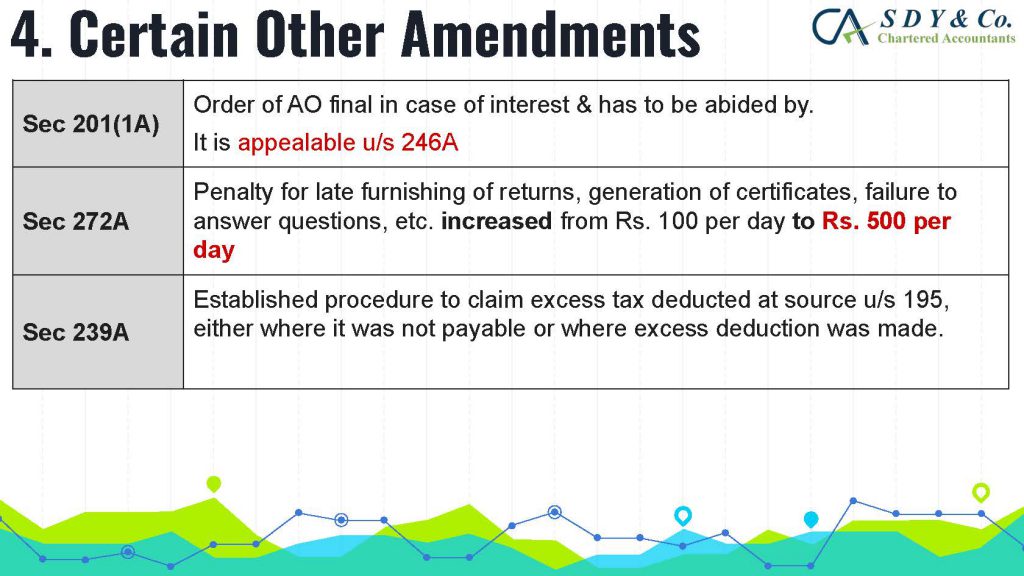
The concept of Pure Agent and its conditions under GST Act is often a topic of confusion in the industry, particularly in cases of reimbursement of expenses. Rule 33 of CGST Rules 2017 explains that if the conditions are met, the expenditure or costs incurred by a supplier as a pure agent of the recipient of supply shall be excluded from the value of supply and will not be taxable.
The conditions for acting as a pure agent are:
(i) the supplier must act as a pure agent of the recipient of the supply and make the payment to the third party on authorization by the recipient
(ii) the payment made by the pure agent on behalf of the recipient of supply has been separately indicated in the invoice issued by the pure agent to the recipient of service
(iii) the supplies procured by the pure agent from the third party as a pure agent of the recipient of supply are in addition to the services he supplies on his own account.
Illustration- CA firm XYZ is engaged to handle the legal work pertaining to the incorporation of Company ABC Pvt. Ltd. Other than its service fees, XYZ also recovers from ABC, registration fee and approval fee for the name of the company paid to the Registrar of Companies. The fees charged by the Registrar of Companies for the registration and approval of the name are compulsorily levied on ABC. XYZ is merely acting as a pure agent in the payment of those fees. Therefore, recovery of such expenses is a disbursement and not part of the value of supply made by XYZ to ABC. “
The term “pure agent” refers to a person who enters into a contractual agreement with the recipient of supply to act as his pure agent to incur expenditure or costs in the course of supply of goods or services or both, and who neither intends to hold nor holds any title to the goods or services or both so procured or supplied as a pure agent of the recipient of supply. The pure agent should not use the goods or services so procured for his own interest, and should only recover the actual amount incurred to procure such goods or services in addition to the amount received for the supply he provides on his own account.
It is important to note that there should be a single invoice raised to the recipient for reimbursement of cost incurred and for the value of supply provided by the supplier for his/her service, and reimbursement should be separately indicated in the invoice. Also, the nature of supply procured by the pure agent from the third party as a pure agent of the recipient should be in addition to the services which he/she supplies on his own.
In cases where the applicant cannot prove that he was authorized to make the payment, or where there are two different invoices for reimbursement and for services provided by the supplier, the status of pure agent may be denied. However, if all the conditions are met, the expenditure or costs incurred by the supplier as a pure agent of the recipient of supply shall be excluded from the value of supply and will not be taxable.
So, we have dealt with main rule, we will go ahead with Explanation which deals with What is Pure Agent for purpose of
Rule 33
a. Contractual Agreement: Supplier should enter into contractual agreement with Recipient to act as Pure Agent to incur expenditure or cost
b. Ownership of Goods/Services: Pure Agent should hold or there should not be any intention to hold the Tile of Goods/Services procured as Pure Agent from third Person
c. Own Use: Pure Agent should not use the goods/services so procured for Own Use
d. Actual Amount: Pure Agent should receive the exact amount of cost/expenditure incurred in relation to procurement of goods/services, and there should not be any profit component while recovering such amount